Car financing options open up a world of possibilities when it comes to getting behind the wheel. From loans to leases and dealer financing, the choices are endless. Let’s dive in and uncover the best option for you.
Whether you’re a first-time buyer or looking to upgrade, understanding the ins and outs of car financing is crucial.
Overview of Car Financing Options
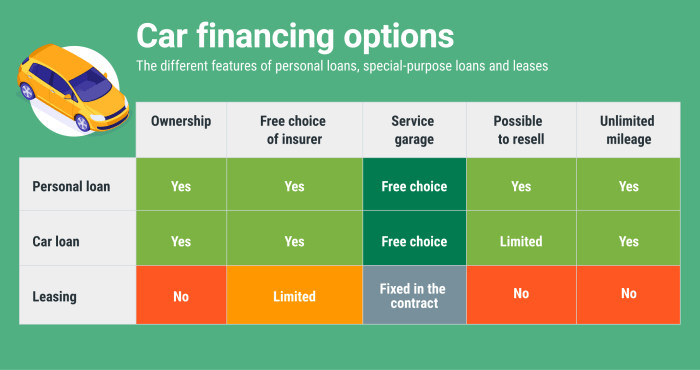
Car financing is the process of obtaining funds to purchase a vehicle through various methods such as loans, leases, or dealer financing. Each option has its own set of pros and cons that individuals should consider before making a decision.
Types of Car Financing Options
- Loans: This involves borrowing money from a financial institution to purchase a car. The buyer then repays the loan amount plus interest over a set period of time.
- Leases: Leasing a car allows the individual to use the vehicle for a specified period by making monthly payments. At the end of the lease, the car is returned to the dealer.
- Dealer Financing: Dealerships offer financing options directly to customers, often through partnerships with financial institutions. This can be a convenient option, but may come with higher interest rates.
Pros and Cons of Car Financing Options
- Loans:
- Pros: Ownership of the vehicle, ability to customize, no mileage restrictions.
- Cons: Higher monthly payments, depreciation affects resale value, potential for negative equity.
- Leases:
- Pros: Lower monthly payments, access to newer vehicles, no worries about depreciation.
- Cons: Mileage restrictions, no ownership at the end of the lease, possible extra fees.
- Dealer Financing:
- Pros: Convenient, may offer promotions or incentives, quick approval process.
- Cons: Higher interest rates, limited negotiation power, potential for add-on products.
Car Loan Options
When it comes to financing a car, one common option is to obtain a car loan. This involves borrowing money from a financial institution to purchase a vehicle and then paying it back over time with interest.
Secured Loans
Secured car loans require the borrower to provide collateral, such as the car itself, to secure the loan. If the borrower fails to make payments, the lender can repossess the vehicle to recoup their losses.
Unsecured Loans
Unsecured car loans do not require collateral, but they often come with higher interest rates to offset the risk for the lender. These loans are based on the borrower’s creditworthiness and financial history.
Balloon Loans
Balloon loans involve lower monthly payments throughout the loan term, but a large “balloon” payment is due at the end. This option can be risky as the borrower needs to have a plan for paying off the remaining balance.
Examples of financial institutions that offer car loans include banks like Wells Fargo, credit unions like Navy Federal Credit Union, and online lenders like Capital One Auto Finance.
Car Lease Options
Car leasing is a type of car financing where you essentially rent a vehicle for a set period of time, typically 2-4 years, and make monthly payments. At the end of the lease term, you have the option to return the car or purchase it at a predetermined price. This differs from buying a car outright, where you own the vehicle once you finish making payments.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Leasing a Car
When it comes to leasing a car, there are both pros and cons to consider:
- Benefits:
- Lower monthly payments compared to buying
- Ability to drive a new car every few years
- Warranty coverage for most repairs
- Drawbacks:
- No ownership of the vehicle at the end of the lease
- Potential for extra fees if you exceed mileage limits or return the car with damages
- Restrictions on customization or modifications
Residual Value in Car Leases
Residual value is the estimated value of the car at the end of the lease term. This value plays a crucial role in determining your monthly lease payments. The higher the residual value, the lower your monthly payments are likely to be. It’s important to understand how residual value is calculated and negotiate this aspect of the lease agreement to potentially save money in the long run.
Dealer Financing: Car Financing Options

When it comes to buying a car, dealer financing is an option that many people consider. This type of financing involves getting a loan directly from the car dealership where you are purchasing the vehicle.
Advantages of Dealer Financing
- Convenience: Dealer financing is convenient because you can arrange your loan and purchase your car in one place.
- Possible Incentives: Dealerships often offer promotions or incentives, such as 0% financing, to entice buyers.
- Quick Approval: Dealer financing can sometimes be approved faster than a traditional bank loan.
Disadvantages of Dealer Financing
- Higher Interest Rates: Dealership financing may come with higher interest rates compared to other lenders.
- Limited Options: You may be limited to the financing options offered by the dealership, potentially missing out on better deals elsewhere.
- Possible Pressure: Some dealerships may use financing as a way to upsell additional products or services.
Tips for Negotiating Favorable Terms
- Do Your Research: Before visiting the dealership, research current interest rates and loan terms so you know what to expect.
- Shop Around: Don’t settle for the first financing offer you receive. Compare rates from multiple lenders to ensure you’re getting the best deal.
- Negotiate the Price First: Focus on negotiating the price of the car before discussing financing terms to avoid confusion.
- Read the Fine Print: Make sure to carefully review all loan documents before signing to understand the terms and conditions.