Using A/B Testing in Marketing, dive into the world of optimizing strategies with this cool, engaging approach that will keep you hooked from the get-go.
Learn about the process, best practices, and common mistakes to avoid in A/B testing for marketing campaigns.
Introduction to A/B Testing: Using A/B Testing In Marketing
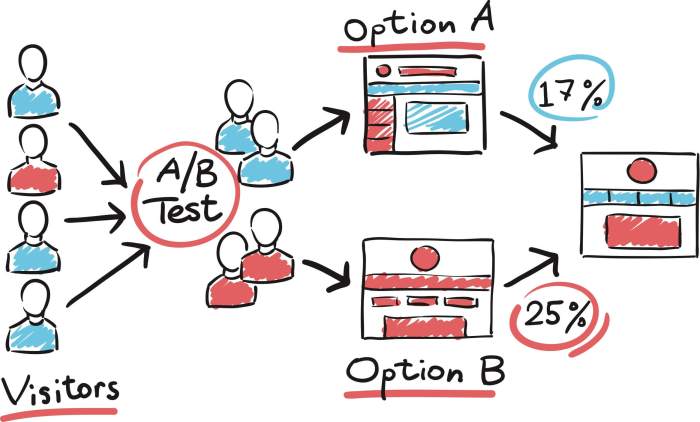
A/B testing, also known as split testing, is a method used in marketing to compare two versions of a webpage, email, or other marketing elements to determine which one performs better. By randomly showing these variations to different segments of the audience, marketers can analyze which version drives more conversions, clicks, or other desired actions.
Examples of Effective A/B Testing
- Testing different call-to-action buttons to see which one generates more clicks.
- Testing variations of email subject lines to determine which one has a higher open rate.
- Testing different landing page layouts to identify which one leads to more conversions.
The Importance of A/B Testing in Optimizing Marketing Strategies
A/B testing plays a crucial role in optimizing marketing strategies as it provides valuable insights into what resonates best with the target audience. By conducting these tests, marketers can make data-driven decisions to enhance their campaigns, improve conversion rates, and ultimately boost ROI.
Setting up A/B Tests
When it comes to setting up A/B tests, it’s all about creating a solid plan and sticking to it. You need to define your objectives clearly, choose the right variables to test, and follow best practices to ensure accurate results.
Defining Clear Objectives
To start off, defining clear objectives is crucial for any A/B test. You need to know exactly what you want to achieve with your test. Whether it’s increasing click-through rates, improving conversion rates, or enhancing user engagement, your objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Set specific goals for your A/B test, such as increasing email sign-ups by 10% within a month.
- Ensure your objectives are measurable so you can track the success of your test accurately.
- Make sure your goals are achievable and realistic based on your current metrics and resources.
- Ensure your objectives are relevant to your overall marketing strategy and business goals.
- Set a timeline for achieving your objectives to stay on track and measure progress effectively.
Selecting Variables to Test
When it comes to selecting variables to test in your A/B experiments, it’s important to choose wisely. Focus on elements that can have a significant impact on your desired outcomes and avoid testing too many variables at once to prevent confusion and skewed results.
Remember, it’s best to test one variable at a time to accurately identify the impact of each change on your results.
- Start by analyzing your website or marketing campaign to identify potential areas for improvement.
- Choose variables that directly correlate with your objectives, such as changing the call-to-action button color or testing different headline variations.
- Avoid testing minor details that are unlikely to have a substantial impact on your key metrics.
- Prioritize variables based on their potential impact and relevance to your goals.
- Document the variables you plan to test and the rationale behind each choice to maintain clarity and consistency throughout the testing process.
Implementing A/B Testing in Campaigns
When it comes to implementing A/B testing in marketing campaigns, there are several key steps to follow in order to ensure success. By carefully setting up and analyzing your tests, you can gain valuable insights into what resonates with your audience and drives conversions.
Choosing Variables to Test
- Determine the specific elements of your campaign you want to test, such as headlines, call-to-action buttons, images, or email subject lines.
- Ensure that each variable you choose to test is distinct and has the potential to impact the overall performance of your campaign.
Creating Variations, Using A/B Testing in Marketing
- Develop multiple versions of the variable you are testing, making sure that each variation is unique and offers a different approach or message.
- A/B testing tools can help you easily create and deploy these variations to your audience.
Setting Up the Test
- Randomly divide your audience into equal segments and assign each segment to one of the test variations.
- Ensure that your test runs for a long enough period to gather sufficient data and account for any fluctuations in traffic.
Analyzing and Interpreting Results
- Monitor key metrics such as click-through rates, conversion rates, and revenue generated to determine which variation performs best.
- Statistical significance is crucial in determining the validity of your results – use A/B testing tools to calculate this.
Improving Conversion Rates
- Once you have identified the winning variation, implement it across your campaign to maximize conversions.
- Continue to iterate and test new variables to continually optimize your marketing efforts and drive better results.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When conducting A/B tests, it’s crucial to steer clear of common pitfalls to ensure accurate results and meaningful insights. Understanding the importance of statistical significance and avoiding biased outcomes are key factors in successful A/B testing.
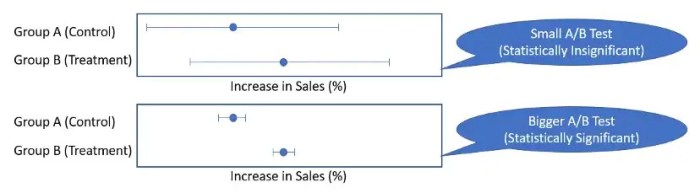
Ignoring Statistical Significance
Statistical significance is vital in A/B testing as it helps determine whether the results observed are due to actual differences in the variations or simply by chance. Failing to account for statistical significance can lead to erroneous conclusions and misguided decision-making. It’s essential to calculate the sample size needed for a test to achieve statistically significant results before drawing any conclusions.
Avoiding Biased Results
Biased results can skew the outcome of A/B tests, rendering them ineffective. Biases can arise from various sources such as sample selection, external factors, or even human error. To avoid biased results, it’s crucial to randomize the assignment of test groups, ensure a representative sample, and eliminate any external influences that could impact the test results. By maintaining objectivity and rigor throughout the testing process, you can mitigate the risk of biased outcomes and obtain reliable data for decision-making.